As a pet owner, ensuring your furry friend’s health is a top priority. Sometimes, pets may show subtle signs of illness that aren’t immediately obvious, making it challenging to identify the underlying issue. This is where pet diagnostic imaging comes into play. With advanced imaging techniques, veterinarians can provide more accurate diagnoses, leading to more effective treatment plans. In this article, we will explore key tools and techniques used in pet diagnostic imaging and their role in providing accurate health assessments for your beloved pets.
What is Pet Diagnostic Imaging?
Pet diagnostic imaging refers to the use of specialized technology and tools to create visual representations of a pet’s internal structures, including organs, bones, and tissues. These images help veterinarians identify abnormalities, injuries, or diseases that may not be visible during a routine physical exam. Diagnostic imaging provides an essential non-invasive method to assess the overall health of your pet, enabling quicker diagnoses and targeted treatments.
Do you want to visit Haridwar? travel agents in Haridwar is the right place to plan your tour. You can book your tour from here.
Common Pet Diagnostic Imaging Techniques
There are several key imaging techniques that veterinarians use to assess your pet’s health. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common methods:
1. X-Rays (Radiographs)
X-rays are one of the most commonly used diagnostic imaging tools in veterinary medicine. They are especially effective in examining bones and joints and can help identify fractures, arthritis, tumors, and signs of infections. X-rays are also helpful for detecting problems with the pet’s chest and abdomen, such as lung diseases or gastrointestinal blockages.
Do you want to visit char dham? char dham tour operator is the right place to plan you Char Dham tour. You can book you tour from here.
How It Works: X-rays use electromagnetic radiation to capture images of the internal structures of the body. Different tissues absorb the radiation at varying rates, which creates a contrasting image. Dense tissues like bones appear white, while softer tissues, such as muscles and organs, show up in shades of gray.
Benefits:
Do you want to visit Indiar? tour operator in India is the right place to plan your tour. You can book your tour from here.
- Quick and efficient for diagnosing skeletal issues
- Helps detect foreign objects in the body
- Non-invasive procedure
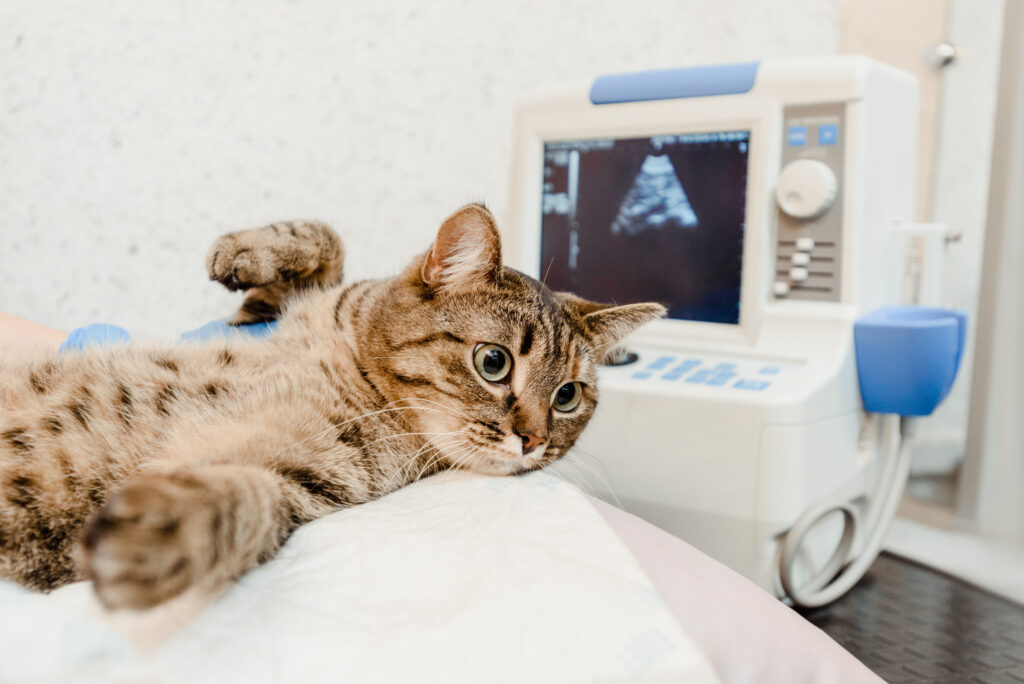
2. Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of soft tissues inside the body. It’s commonly used to assess organs like the heart, liver, kidneys, and bladder, and is often used to evaluate pregnancy in female pets.
How It Works: A small probe, called a transducer, is placed on the pet’s skin (usually with a conductive gel). The transducer sends out high-frequency sound waves, which bounce off tissues and organs to create a live image on a screen. The technician or veterinarian can then view the organs’ shape, size, and any abnormalities in real-time.
Benefits:
- Ideal for examining soft tissues such as organs, blood vessels, and reproductive organs
- Real-time imaging allows for immediate diagnosis
- Non-invasive, with no radiation exposure
3. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
MRI is one of the most advanced diagnostic imaging tools available, particularly for soft tissues like the brain, spinal cord, muscles, and ligaments. It is often used in complex cases such as neurological issues, spinal problems, or tumors in soft tissues.
How It Works: An MRI machine uses strong magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the internal structures. Unlike X-rays, MRI scans do not use radiation, making them safer for sensitive tissues. The images produced are highly detailed and can be used to assess a pet’s brain, spine, or joints.
Benefits:
- Provides high-resolution images of soft tissues
- Ideal for detecting brain and spinal cord abnormalities
- Non-invasive and does not involve radiation
4. CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
CT scans, also known as CAT scans, are similar to X-rays but provide more detailed images by taking multiple X-ray images from different angles and combining them to create cross-sectional views of the body. This technique is particularly useful for diagnosing issues related to the chest, abdomen, and head.
How It Works: The pet is placed in a large machine, which takes several X-ray images. These images are then processed by a computer to create detailed cross-sectional images (slices) of the body. The veterinarian can view these slices to pinpoint the exact location and size of an issue.
Benefits:
- Provides detailed cross-sectional images of organs and tissues
- Helps diagnose tumors, infections, and internal bleeding
- Can assist in planning surgeries by showing a detailed view of the affected area
5. Endoscopy
Endoscopy is a diagnostic technique that involves using a long, flexible tube equipped with a camera (endoscope) to visually inspect the internal structures of the body. This technique is commonly used to examine the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system, and urinary tract.
How It Works: A small incision or natural body opening (such as the mouth or anus) is made, and the endoscope is inserted to examine the area. The camera transmits real-time images to a monitor, allowing the veterinarian to see the condition of the organs and identify any abnormalities.
Benefits:
- Allows direct visualization of internal structures without needing surgery
- Useful for diagnosing gastrointestinal issues, lung problems, and foreign object ingestion
- Can be combined with biopsy for tissue sampling
When Is Pet Diagnostic Imaging Needed?
Veterinarians may recommend diagnostic imaging in a variety of scenarios, including:
- Signs of Injury: If a pet is in an accident or has sustained trauma, imaging can help identify fractures, internal bleeding, or organ damage.
- Chronic Symptoms: Symptoms like persistent coughing, vomiting, diarrhea, or lameness may require imaging to identify the underlying cause.
- Unexplained Weight Loss or Lethargy: Imaging can help identify infections, tumors, or metabolic diseases that may be contributing to a pet’s condition.
- Pre-Surgical Planning: In some cases, imaging is used before surgery to help determine the extent of a problem and plan the most effective surgical approach.
The Benefits of Pet Diagnostic Imaging
- Early Detection of Health Issues: Pet diagnostic imaging can detect health problems early, often before symptoms become severe, giving pets the best chance at a full recovery.
- Minimally Invasive: Many imaging techniques, like ultrasound and MRI, are non-invasive, reducing stress and discomfort for your pet.
- Accurate Diagnosis: Imaging provides clear, detailed visuals of internal structures, allowing for a more accurate diagnosis and better treatment planning.
- Better Treatment Planning: With detailed images, veterinarians can tailor treatment plans more effectively, whether it involves medication, surgery, or other interventions.
Conclusion
Pet diagnostic imaging is a vital tool in modern veterinary care, offering invaluable insights into the health and well-being of your pet. By utilizing techniques like X-rays, ultrasounds, MRIs, and CT scans, veterinarians can diagnose conditions that might otherwise remain undetected. Whether your pet needs an imaging exam for an injury, chronic health condition, or pre-surgical evaluation, these diagnostic tools can make all the difference in ensuring your pet receives the best care possible. If you notice any concerning signs in your pet, consult your veterinarian to see if diagnostic imaging is necessary to pinpoint the cause and develop an effective treatment plan.